How to ensure your team can securely connect to your company’s internal network while working from home or traveling? Whether your employees are connecting from a home network or a branch office, you need a remote work setup that allows them to access headquarters resources safely and efficiently.
This remote work setup guide will walk you through the essentials. You don’t need to be an expert—just follow this step-by-step guide to get a comprehensive, hands-on tutorial for creating a secure remote work environment.
What are the Core Components of Remote Work Setup?
Right Device and Distraction-Free Workspace
A successful remote work setup begins with providing the right devices for your employees. This includes not only a computer, wireless keyboard and mouse, and monitor, but also a comfortable desk and a quiet, distraction-free workspace. Encourage your team to create a pleasant environment—for example, playing soft background music or keeping a cup of coffee or tea nearby—to help maintain focus and productivity.
Equally important is a stable internet connection. Unstable networks can disrupt meetings, slow down data transfers, and affect communication. To maintain a smooth workflow, it’s recommended to use a reliable and high-speed connection whenever possible.
In some industries or large organizations, specific hardware and software requirements may apply. Ensure your employees only use devices and programs approved or officially registered by your company to maintain security and compliance in your remote work setup.
Network and Information Security Preparation
Remote work has blurred the boundaries of corporate networks, making remote work security more challenging than ever. According to industry reports, over 60% of companies have experienced some form of cybersecurity threat during periods of remote work setup.
Therefore, organizations need to develop a comprehensive remote work security strategy in collaboration with employees. Strengthen cybersecurity awareness training so employees can identify phishing emails, create strong passwords, and safely access company resources even when using public networks.
Companies should also deploy firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and antivirus gateways to defend against external attacks. Internally, implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) solutions to centrally manage devices, control access permissions, and encrypt data transmissions. By ensuring both network and device protection, your secure remote work setup becomes resilient against common security threats.
Employee Management and Productivity
Regardless of the form of remote work, effective employee management is essential to maintaining team performance and operational efficiency. The shift in work style brings new management challenges. You can no longer directly monitor employees’ execution and progress, which may lead to delayed feedback and slower decision-making. In addition, employees with stronger social needs may experience isolation or anxiety due to reduced in-person interaction, affecting their mental well-being and motivation.
To address these challenges, companies should combine structured management systems with supportive tools. For example, establish clear performance frameworks (OKRs/KPIs) and use some employee monitoring software to track progress; conduct regular online meetings and feedback sessions to maintain transparency; and provide psychological support and virtual training to enhance employees’ sense of belonging and growth. With balanced attention to both efficiency and well-being, remote teams can sustain long-term cohesion and productivity.
Four Main Remote Access Methods
Once you’ve prepared all the essentials above, the next step in your remote access setup is to securely connect to internal resources—such as file servers, ERP systems, or development environments—while employees are working outside the office.
There are several ways to establish a secure remote connection, including port mapping and NAT traversal tools, VPN connections, remote desktop software, and SD-WAN solutions. While implementing these solutions is primarily the responsibility of your technical team, as a leader or manager, it’s important for you to understand the advantages and limitations of each approach to make informed decisions for your company.
Method 1: Port Mapping and NAT Tools
Best for: Quick or temporary access to a single internal service
NAT traversal tools have become a popular remote access setup solution. Using this technology, you can bypass NAT and firewalls to allow your employees to connect directly to internal network resources.
These tools are easy to use, support remote access between devices, and do not require a public IP address. This method is suitable for both businesses and individual users within your organization. The most commonly used tool is NAT123.
How to Set Up Remote Access with NAT123
Setting up remote access via NAT123 is straightforward:
- Install and configure the NAT123 client software on the internal machine your employees need to access.
- Create a custom mapping rule that assigns a specific domain and port to the internal service (for example, your internal web server or database).
- Log in to your NAT123 account and activate the mapping.
- From outside the office, employees can connect using the provided public domain and port to securely access internal resources.
 Cons
Cons- Very easy to set up
- No public IP required
 Pros
Pros- Data passes through third-party servers
- Security and stability depend on the provider
Method 2: VPN
Best for: companies needing secure, full access to internal network resources
VPN is the most common method in a remote work setup to connect securely to company internal network. With a VPN, you can create an encrypted connection so employees can safely access internal resources from anywhere.
If your company uses a hardware firewall or gateway, you can typically enable VPN services directly through the firewall, such as PPTP or IPSec VPN. In the firewall’s management interface, you can usually:
- Enable the VPN service (e.g., PPTP),
- Set up username and password authentication,
- Configure NAT mapping for the internal hosts.
Most firewall devices have similar configuration steps, making this method quite standard. If you have a network administrator or IT team, this provides a reliable way for your employees to access internal resources securely.
 Cons
Cons- High security with encrypted data transfer
- Controlled access to internal network resources
 Pros
Pros- Complex configuration
- May be affected by network restrictions or bandwidth limitations
Method 3: Remote Desktop Software
Best for: Using specialized software or full work environments remotely
Remote Desktop tools like Windows Remote Desktop, TeamViewer, or AnyDesk allow your employees to control office PCs from anywhere, mirroring their desktop environment as if they were at their desks.
This is especially useful when your team needs access to software or files only installed on office machines or when your work environment is tightly controlled. Remote desktop solutions also enable real-time collaboration—multiple team members can access shared machines for troubleshooting, demos, or testing.
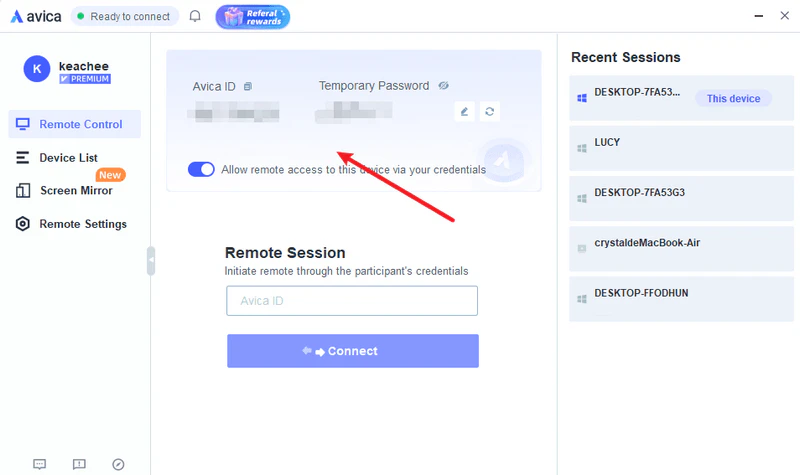
Avica Remote Work Tool
Avica is a high-performance remote desktop tool ideal for teams that prioritize low latency and cross-platform flexibility. Follow the steps below to remotely access your office computer:
- Install the Avica client on both your office and home devices (desktop and mobile supported).
- Log in with the same account, then enter the Avica ID of the office device.
- Click Connect.
Windows Remote Desktop
On office PC:
- Enable Remote Desktop in Settings → System → Remote Desktop.
- Set a strong Windows password.
- Have IT map your PC’s RDP port (default 3389) through your company router.
On home PC:
- Open Remote Desktop Connection.
- Enter your company’s public IP and port.
- Log in with your Windows credentials.
Chrome Remote Desktop
A simpler, cross-platform option that requires no port forwarding.
- Install the Chrome Remote Desktop extension on the work computer, name the device, and create a PIN.
- On the home computer, log into the same Google account and connect via the Chrome Remote Desktop website.
 Cons
Cons- Very easy to set up
- Full desktop control
 Pros
Pros- Office PC must remain powered on
- Performance depends on network quality
Method 4: SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network)
Best for: Medium to large enterprises with strict security and performance needs.
Apart from VPN, port mapping, or remote desktop software, your company can also use dedicated routing devices and SDN (Software-Defined Networking) technology to achieve cross-region network connectivity across different ISPs. This allows your employees to access ERP, OA, and other internal systems without changing your existing network architecture.
SD-WAN is a modern, enterprise-level networking solution, particularly suitable if your company has multiple locations or numerous branch offices. It is ideal for scenarios requiring high network reliability, low latency, and strong application performance, such as cloud computing, real-time video conferencing, and VoIP communications.
For example, you can use the AC3000-1000 router as the main node and M50 routers as sub-nodes.
1. Configure the Main Node (AC3000-1000)
- Log in to AC3000-1000 → [SD-WAN] → [Server Configuration].
- Set mode to Main Node, enter SD-WAN account and password, then click Connect.
- Once connected, go to [Server Access Permissions] → Add, define sub-node access IP ranges (e.g., Finance: 192.168.0.100–192.168.0.200).
- Optional: Refine access in [Permission Settings].
- Set up Group Policy under [Permission Management] → [Group Policy], assign permission rules, and set upload/download limits.
- Assign sub-nodes to the configured policy under [Device Group].
2. Connect Remote Devices
Personal Users: Install “Cloud Connect Personal Client” on the home computer, log in, and access HQ resources.
Branch Offices / Multiple Users
- On M50 router → [SD-WAN], enable SD-WAN client, enter main node account, and click Confirm.
- Main node: approve branch under [SD-WAN] → [Network Topology] → [New Device Requests].
- Assign the branch node to the appropriate permission group.
- All devices under the branch node can now access HQ resources as if they were on-site.
 Cons
Cons- Cross-region, multi-ISP access without changing existing network
- Centralized permission management
- Supports both individual and branch office users
 Pros
Pros- Higher cost
- Requires dedicated hardware
6 Steps to Build a Secure Remote Work Environment
No matter which remote access method your company chooses, following these seven steps will help protect both your company’s data and your employees’ personal workspaces.
Step 1: Confirm and Protect Work Devices
Ensure that all devices used for work remain secure at all times.
For enterprises, it’s best to verify that each employee device is approved for remote work. The most convenient way is to use endpoint management solutions like AnySecura: when personal computers connect directly to the company network via VPN, you can require the client to be installed—devices without it can be denied access. AnySecura can also perform security checks to ensure the device meets company security requirements, and block access if it does not. Once connected, it can manage, control, and audit all employee activity, prevent risky behavior, and encrypt confidential files, even in remote environments.
If providing dedicated company-issued devices is not feasible, require employees to install and regularly update trusted antivirus software, such as Microsoft Defender. Enable automatic system and application updates to apply critical patches, and encrypt hard drives using BitLocker (Windows) or FileVault (macOS) to protect sensitive company data, even if a device is lost or stolen.
Step 2: Fortify Your Network
Before arranging remote work, your company should instruct employees to change the default router credentials on their home networks, such as “admin/admin,” to strong, unique passwords, and ensure Wi-Fi is protected with WPA2 or WPA3 encryption. Employees should also regularly check their routers for firmware updates to patch vulnerabilities. By securing home networks from the start, you minimize the risk of unauthorized access to your company’s resources.
Step 3: Strengthen Identity Authentication and Set Privileges
Your employees’ digital identities are the keys to your company’s systems. You are suggested to deploy a company-wide password manager, such as 1Password or Bitwarden, to securely store and manage credentials, and enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) on all essential accounts—particularly email, cloud platforms, and work-related logins.
If you consider that passwords and MFA alone are not enough, then implement data classification and role-based access control: assign employees access only to the information necessary for their role, and require higher-level approvals for sensitive or confidential data.
Step 4: Stay Alert and Practice Smart Internet Habits
Cyber threats often exploit human error, so your company must cultivate awareness. Train employees to recognize phishing emails—attackers may impersonate supervisors or IT staff. Instruct them to verify URLs before clicking and avoid opening unexpected attachments. By developing these cautious habits across your workforce, you reduce the risk of malware infection and credential theft.
Step 5: Store and Sync Data Securely in the Cloud
Direct your employees to save and back up work using company-approved cloud platforms such as OneDrive, SharePoint, or Google Drive. These platforms facilitate remote collaboration and provide version history, enabling file recovery in case of accidental deletion or ransomware attacks. Centralized cloud storage ensures data integrity and supports overall team productivity.
Step 6: Protect Physical Workspace
Physical security is as important as digital safety. Instruct employees to use privacy filters in public spaces and to lock computers when stepping away (Win + L or Control + Command + Q). Avoid sharing company devices with family or friends to maintain professional data isolation and prevent accidental data exposure.

A simple guide on how to monitor employees working from home, including productivity tracking, basic rules, and how to avoid invading privacy.Learn more>>
Enterprise-Grade Protection: AnySecura DLP and Employee Monitoring Solution
While employee awareness is critical, it is not sufficient. With diverse devices and unpredictable home networks, controlling corporate data requires professional endpoint and data protection systems like AnySecura.
1. Transparent File Encryption
AnySecura encrypts core business documents—designs, contracts, source code—so they remain protected even if copied or sent outside your corporate network.
Files can only be opened on authorized company devices; elsewhere, they appear as unreadable gibberish.
2. Fine-Grained Access Control
Not every employee needs access to all resources. AnySecura allows your company to:
- Restrict departments to specific folders or IP ranges.
- Prevent data copying to USB drives or cloud storage.
- Control actions such as print, copy, or screenshot based on role.
This least-privilege approach minimizes internal and external risks.
3. Behavior Monitoring and Auditing
AnySecura tracks all endpoint activities:
- File operations: who opened, modified, or deleted what.
- Network behavior: visited websites, chat logs, email records.
- Device usage: external drive activity.
- Screen capture: real-time view or playback for forensic purposes.
Detailed audit trails help your company identify suspicious behavior early and provide evidence if data breaches occur.
With AnySecura, your company can empower employees to work remotely while maintaining full control over data security—achieving true peace of mind.

Explore top remote management tools in 2026 and find the best fit for security, IT support, and hybrid work. Learn more>>
FAQs about Remote Work Setup
What is remote work set up?
Remote work setup refers to a combination of physical space, hardware, software tools, and work habits established in a non-traditional office location (usually at home or elsewhere) to achieve efficient, safe, and comfortable work.
What is the best setup for working from home?
A fixed corner, a chair that allows you to straighten your back (with a lumbar support), a laptop stand + external keyboard and mouse, a smooth network access, a large monitor, an external camera, and a professional microphone.
Conclusion
By understanding different remote access methods and implementing the six essential security steps outlined above, you’ll find that creating a secure home office for your team isn’t complicated. Think of it as a checklist—small steps taken by your company that make a significant difference in protecting data and maintaining productivity.


