For a long time, backups have been considered as the "last line of defense" for data security. However, the reliability of traditional backups is significantly undermined by two core risks:
- Ransomware attacks often prioritize targeting and corrupting backup data.
- Improper operations or privilege misuse can lead to accidental deletion or alteration of backups.
Consequently, a growing number of enterprises have realized that successful data recovery depends not merely on having backups, but on ensuring that the backup data itself remains protected and available. Traditional backup mechanisms are increasingly inadequate in meeting today's demands for data security and recovery requirements. Against this backdrop, Immutable Data Backup has emerged as a critical pillar of modern data protection architectures.
What Is Immutable Data Backup?
Immutable Data Backup is a data protection mechanism designed around the core principle of "immutability". It employs technical measures to enforce strict lifecycle controls over backup data, ensuring that once created, data cannot be modified, deleted, or overwritten during a preset retention period. Even in the event of malicious attacks, operational errors, or privilege abuse, backup data remains in its original state and can be used for reliable recovery.
Unlike traditional backups that rely on management policies, procedures, and human discipline, Immutable Data Backup enforces immutability through underlying technical mechanisms, enhancing and securing the integrity of backups.
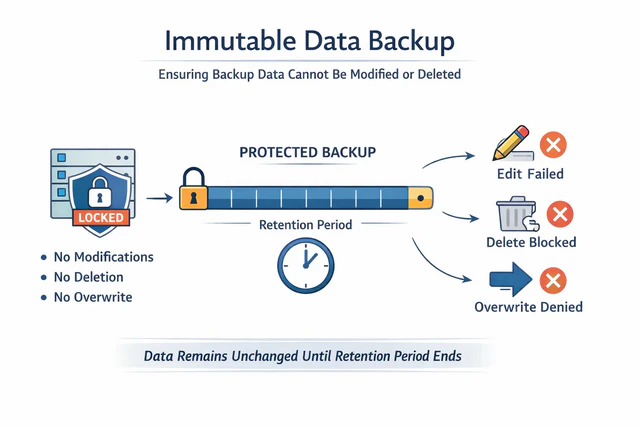
Immutable Data Backup vs. Traditional Backup: A Shift in Trust
Immutable Data Backup is not simply an enhancement of traditional backup. Its fundamental difference lies in a shift in the trust model. In traditional backup systems, backup security depends heavily on permission management, operational processes, and human behavior. As long as individuals hold the relevant permissions, they can perform operations such as deletion or modification on the backup data. The security of this model depends on a critical premise: permissions must be used correctly, and operators must always remain trustworthy. Once this premise is broken, the security of the model becomes fundamentally compromised.
In contrast, Immutable Data Backup adopts a fundamentally different design philosophy. It applies technical constraints to backup data, making actions like deletion, modification, or overwriting logically impossible to execute. This transforms the security of backups from being dependent on "trust in people" to being grounded in "trust in technology".
Key Differences at a Glance:
| Dimension | Traditional Backup | Immutable Data Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Data Locking | Modification and deletion allowed with permissions | Locked after write, immutable during retention |
| Ransomware Resistance | Limited, backups are vulnerable | Strong, immutability blocks backup destruction |
| Recovery Reliability | Low, risk of tampering or deletion | High, data always remains in original state |
| Protection against mistakes | Relies on audits and procedures | Built-in, automatic enforcement |
This shift—from human trust to technical trust—is the core and defining value of Immutable Data Backup.
How Immutable Data Backup Enforces Data Integrity
Immutability is not achieved through a single mechanism, but through multiple technologies working together to ensure backup data remains unchanged during critical time windows. The core mechanisms include:
1. Write Once, Read Many (WORM)
During the backup generation phase, once data is written to the storage medium, it is marked as read-only for a preset retention period. The system does not allow deletion, modification, or overwriting to the existing data. This mechanism ensures that historical backups cannot be altered by subsequent writes, system failures, or malicious activities, thereby providing a stable and traceable foundation for data recovery.
2. Retention Lock
Immutability is retention-based, not permanent.
- During the retention period, deletion and modification are strictly prohibited
-
After the retention period expires, backup data returns to a manageable state and can be:
- Deleted to free storage space
- Migrated to archival storage
This approach enforces strong protection during high-risk periods while preserving flexibility and cost control over the long term.
3. Privilege Neutralization
Immutable Data Backup employs underlying constraints to neutralize the destructive potential of permissions themselves. Even if an attacker gains administrator or system-level access, they cannot bypass immutability constraints to delete or tamper with backup data. This fundamentally reduces risks caused by credential compromise or privilege abuse.
Together, these mechanisms form the technical foundation of Immutable Data Backup, making it no longer reliant on manual controls.
Limitations and Considerations
While Immutable Data Backup greatly improves backup reliability, it is not a universal solution and has certain limitations:
1. Higher Storage Costs
Immutable backups typically use append-only writes, meaning data can only grow during the retention period and cannot be overwritten. Over time, this leads to increased storage consumption. Organizations must balance security and cost by carefully designing retention policies.
2. Reduced Recovery Flexibility
Because backups cannot be modified or deleted during the retention period:
- Incorrect or redundant backups cannot be quickly removed
- Corrections usually require creating new backup versions or marking errors
For environments requiring extreme flexibility—such as rapidly iterating test systems—immutable backups may be less suitable than mutable alternatives.
3. Not a Replacement for a Complete Security Strategy
Immutable Data Backup protects against deletion and tampering, but it does not prevent data leakage, such as unauthorized reading or exfiltration of sensitive data. It must therefore be part of a layered security approach.
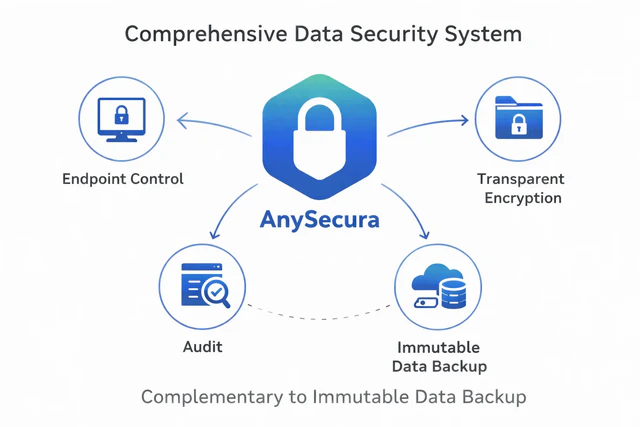
In this regard, AnySecura complements Immutable Data Backup with comprehensive protection capabilities:
- Endpoint Control: Centralized permission and policy enforcement ensures only authorized users can access backup data
- Transparent Encryption: Data is encrypted at rest and in transit without impacting user experience
- Operation Auditing: All access and actions involving backup data are fully logged and traceable
Together, Immutable Data Backup and AnySecura protect not only data integrity, but also access security, traceability, and compliance.

Discover how DLP software delivers compliance, prevents insider threats, and secures sensitive information across endpoints, cloud services, and networks. Learn more>>
Where Immutable Data Backup Delivers the Most Value
Leveraging its core advantages of "immutability, privilege invalidation, and retention-period locking". Immutable Data Backup demonstrates high application value in three key scenarios:
1. Ransomware Defense
Ransomware typically encrypts production data and destroys backups to force ransom payments. With Immutable Data Backup, even if production systems are fully encrypted, backup data within the retention period remains unalterable and can be directly used for business recovery. Combined with AnySecura’s endpoint control and auditing, organizations gain multi-layered protection across endpoints and backups.
2. Internal Threat Mitigation
Privileged administrators, departing employees, or contractors with malicious intent may intentionally damage backup data. Immutable Data Backup ensures that even users with the highest privileges cannot tamper with backups during the retention period, protecting critical intellectual property.
3. Compliance and Auditing
Industries such as finance, healthcare, and government often face stringent regulatory and auditing requirements mandating long-term data retention and immutability. Immutable Data Backup provides a technically enforced retention mechanism, meeting audit, legal, and regulatory compliance needs, thereby reducing enterprise compliance risks.
Conclusion
In an environment where ransomware attacks and operational errors are increasingly common, the key to data protection is no longer "whether backups exist", but whether backups are trustworthy and usable. Traditional backups rely on permissions and human adherence to procedures, making them vulnerable to risks from privilege abuse and malicious attacks. Immutable Data Backup, through write-once protection, retention locking, and privilege neutralization, shifts backup security from being "managed by people" to being "enforced by mechanisms", thereby enhancing the trustworthiness of backup data.
It is important to clarify that Immutable Data Backup is not an "ultimate solution". Its higher storage costs, reduced flexibility, and inability to prevent data leakage mean it must be combined with complementary solutions such as AnySecura. Overall, Immutable Data Backup has become a foundational capability of modern data protection. Only by combining immutability with endpoint control, encryption, and auditing can organizations build a truly resilient data security framework—ensuring business continuity and regulatory compliance.


