- Chapter 1: Introduction
-
Chapter 2: Installation and Deployment
- 2.1 Basic Operating Framework
- 2.2 Software and Hardware Requirements
- 2.3 Installation and Deployment of Server and Console
- 2.4 Installing and Deploying the Repeater
- 2.5 Installing and Deploying the Web Server
- 2.6 Deploying the Client Module
- 2.7 Creating the USB Encryption Client
- 2.8 System Upgrade
- 2.9 Uninstallation
- Chapter 3: Console
- Chapter 4: Statistics
-
Chapter 5: Logs
- 5.1 Basic Event Logs
- 5.2 Application Logs
- 5.3 Web Browsing Logs
- 5.4 Keyword Search Logs
- 5.5 Document Operation Logs
- 5.6 CD/DVD Burning Operation Logs
- 5.7 Shared Document Operation Logs
- 5.8 Remote Desktop Logs
- 5.9 Document Print Logs
- 5.10 Removable Storage Operation Logs
- 5.11 Asset Change Log
- 5.12 Windows System Logs
- 5.13 Policy Logs
- 5.14 System Event Logs
-
Chapter 6: Policies
- 6.1 Introduction to Policies
- 6.2 Basic Policies
- 6.3 Device Control Policies
- 6.4 Application Policies
- 6.5 Web Browsing Policies
- 6.6 Screen Recording Policies
- 6.7 Logging Policy
- 6.8 Remote Control Policies
- 6.9 Custom Configuration Policies
- 6.10 System Alert Policies
- 6.11 Network Traffic Control Policies
- 6.12 Network Control Policies
- 6.13 Email Control Policy
- 6.14 IM File Transfer Policy
- 6.15 Upload Control Policy
- 6.16 Document Operation Policy
- 6.17 Print Control Policy
- 6.18 Removable Storage Authorization Policy
- 6.19 Software Installation Management Policy
- Chapter 7: Monitoring
- Chapter 8: Remote Maintenance
- Chapter 9: Security Monitoring
-
Chapter 10: Sensitive Information
- 10.1 Enable/Disable Sensitive Content Inspection Authorization
- 10.2 Sensitive Information Exfiltration Control Policy
- 10.3 Sensitive Information Local Control Policy
- 10.4 Document Label Policy
- 10.5 Document Classification Permission Policy
- 10.6 Sensitive Information Logs
- 10.7 Document Tag Logs
- 10.8 Sensitive Information Scanning Tools
- 10.9 Full-Disk Sensitive Information Scan Tasks
- Chapter 11: Visual Perception
- Chapter 12: Watermarks
- Chapter 13: Asset Management
-
Chapter 14: Category Management
- 14.1 Application Categories
- 14.2 Website Classification
- 14.3 Time Type Categories
- 14.4 Removable Storage Categories
- 14.5 Network Address Categories
- 14.6 Network Port Categories
- 14.7 Software Installation Package Rule Repository
- 14.8 Software Uninstallation Categories
- 14.9 Email Categories
- 14.10 Sensitive Information Classification Library
- 14.11 Watermark Templates
- 14.12 User Permission Template Categories
- 14.13 Condition Library
-
Chapter 15: Request Management
- 15.1 Desktop Request Management
- 15.2 Encryption Request Management
- 15.3 Superior Approval
- 15.4 Permission Viewing
- 15.5 Request Approval Permission Settings
- 15.6 Self-Record Permission Settings
- 15.7 Self-Record Logs
- 15.8 Desktop Request Document Upload Settings
- 15.9 Client Requests
- 15.10 Client Self-Approval
- 15.11 Proxy Administrator
- Chapter 16: Network Access Detection
- Chapter 17: Data Backup
-
Chapter 18: Tools
- 18.1 Account Management
- 18.2 Computer Management
- 18.3 USB Encryption Client Management
- 18.4 Alert Messages
- 18.5 Mail Report Settings
- 18.6 Network Access Gateway Management
- 18.7 Policy Application Query
- 18.8 Client Tools
- 18.9 Server Time
- 18.10 Relay Server Management
- 18.11 Policy and Library Synchronization Management
- 18.12 Organizational Structure Synchronization
- 18.13 Client Upgrade Management
- 18.14 Options
- Chapter 19: User System Management
- Chapter 20: Audit Console
-
Chapter 21: Document Security Management
- 21.1 Terminology Overview
- 21.2 Operation Workflow
- 21.3 Enable/Disable Encryption Authorization
- 21.4 Authorized Software Management
- 21.5 Secure Zone Management
- 21.6 External Release Object Management
- 21.7 External Release Configuration Template Management
- 21.8 Encryption Permission Settings
- 21.9 Encryption Parameter Settings
- 21.10 Long-Term Offline Authorization Settings
- 21.11 Secure Communication Settings
- 21.12 Encrypted Document Operation Logs
- 21.13 Full-Disk Scan
- 21.14 Document Management
- 21.15 Intelligent Endpoint Management
- 21.16 USBKey Management
- 21.17 Backup Server Settings
- 21.18 Custom Keys
- 21.19 Encrypted Document Backup
-
Chapter 22: Windows Encrypted Client
- 22.1 Client Operating Status
- 22.2 File Explorer
- 22.3 Encrypted Document Scan Tool
- 22.4 Encrypted Files
- 22.5 Decrypt Files
- 22.6 Request Decryption
- 22.7 Read-Only Access
- 22.8 Export
- 22.9 Request Export
- 22.10 Export Extraction
- 22.11 Modify Encrypted Document Security Attributes
- 22.12 Modify Encrypted Document User Permissions
- 22.13 Request Change of Encrypted Document Attributes
- 22.14 View Document Attributes
- 22.15 Request Temporary Offline
- 22.16 View Request Information
- 22.17 Encrypted System Information
- 22.18 Offline Authorization Login
- 22.19 Import License File
- 22.20 Login and Logout of the Encryption System
- 22.21 Parameter Settings
- 22.22 Using the Encryption USBKey
- 22.23 Proxy Administrator
- 22.24 Force Update Policy
- Chapter 23: Linux Encrypted Client
- Chapter 24: Mac Encrypted Client
- Chapter 25: USB Encrypted Client
- Chapter 26: External Viewer
- Chapter 27: Backup Encryption Server
- Chapter 28: Document Storage Request
- Chapter 29: Cloud Document Backup Server
-
Chapter 30: Reporting System
- 30.1 Terminology
- 30.2 Reporting Console
- 30.3 Predefined Reports and Queries
- 30.4 General Report Settings
- 30.5 Report Statistics Content
- 30.6 Template Management
- 30.7 Period Management
- 30.8 Indicator Management
- 30.9 Periodic Reports
- 30.10 Query
- 30.11 Historical Reports
- 30.12 Email Reports
- 30.13 Data Center
- Chapter 31: WEB Console
- Chapter 32: WEB Approval
- Chapter 33: WEB Reports
-
Chapter 34: Software Center
- 34.1 Installation & Deployment
- 34.2 Software Center Server
- 34.2.1 Software Management
- 34.2.2 Software Review
- 34.2.3 My Edit
- 34.2.4 My Applications
- 34.2.5 Installation Management
- 34.2.6 Settings - Category Management
- 34.2.7 Settings - User Management
- 34.2.8 Settings - Permission Management
- 34.2.9 Settings - Advanced Settings
- 34.2.10 Settings - Batch Export
- 34.2.11 Settings - Batch Import
- 34.2.12 Audit Logs
- 34.3 Software Center Client
- 34.4 Software Center Client Logs
- Chapter 35: Security Viewer
- Chapter 36: Security Approval App
- Chapter 37: Dedicated Burning Tool
-
Chapter 38: Access Gateway
- 38.1 Network Architecture
- 38.2 Device Introduction
- 38.3 Device Deployment
- 38.4 Management Interface Overview
- 38.5 Home Page
- 38.6 Network Parameters
- 38.7 Access Gateway Configuration
- 38.8 Server Management
- 38.9 Guest Login Management
- 38.10 Status Information
- 38.11 System Management
- 38.12 Access Gateway Logs
- 38.13 Other Operations
- 38.14 Super Mode
- 38.15 Usage Example
- Chapter 39: Secure Access Gateway
- [email protected]
- 15 Scotts Road, #03-12, Singapore
Overview
To improve work efficiency through IT, many enterprises deploy information management systems such as ERP, OA, CRM, and PLM. These systems store critical company data, including customer information, R&D plans, and financial reports, making them highly valuable. The Secure Access Gateway ensures the security of these applications, preventing confidential corporate information from being easily leaked. It provides comprehensive protection for encrypted documents during upload, download, and transmission through upload decryption, download encryption, and communication encryption.
The Secure Access Gateway has two main functions: Application System Protection and Shared File Protection.
Application System Protection
It protects files on servers of applications like OA, PLM, and SVN. Unauthorized users or programs cannot access the protected servers. Authorized users and programs can access normally, with uploaded files decrypted on the server and downloaded files encrypted on local machines.
Shared File Protection
It protects shared file servers, functioning similarly to application system protection. Unauthorized users or programs cannot access protected servers, while authorized users can. Uploaded files to a designated directory on the shared server are decrypted, and downloaded files from that directory are encrypted. Files in other unspecified directories are not processed.
39.1 Network Architecture
The control functionality of the Secure Access Gateway primarily relies on hardware-based gateway devices. There are two working modes for these devices: Bridge Mode and Router Mode.
Bridge Mode
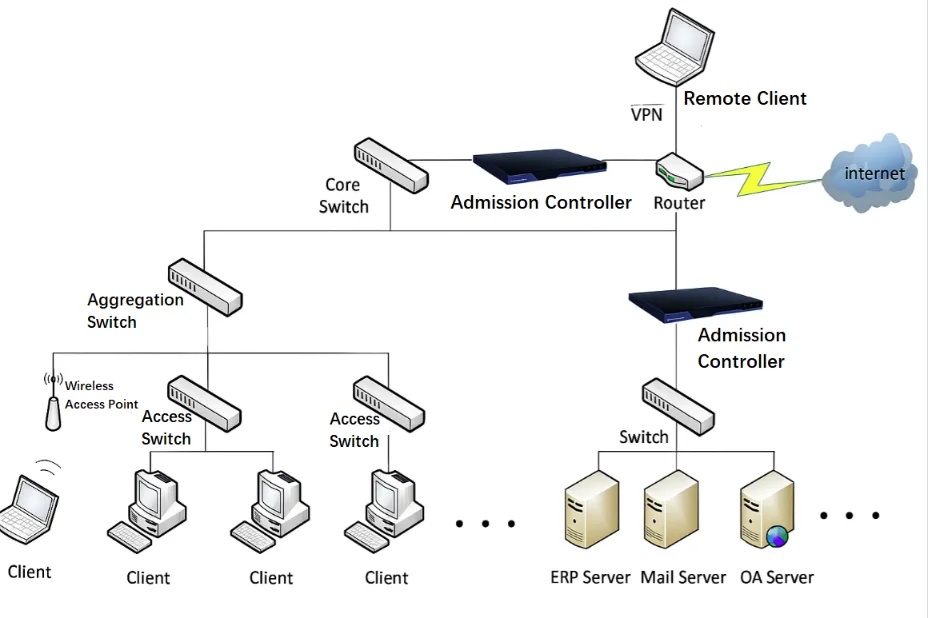
In Bridge Mode, the network structure and configuration remain unchanged. The Secure Access Gateway device is simply inserted into the network at the point where control is needed, typically in front of critical application servers or gateways. This setup allows seamless integration without modifying existing network infrastructure.
Bypass Control Mode
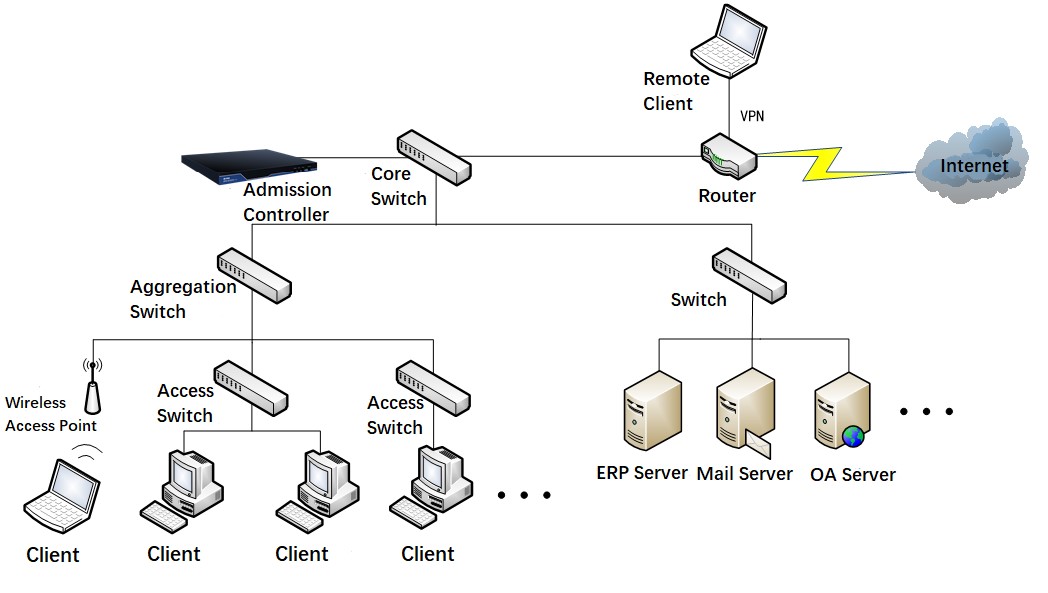
Routing Mode
Enable policy-based routing on the core switch to control inter-subnet access. This control method does not affect the existing network architecture and requires the core switch to support policy-based routing.
Bypass Mirror Mode
Set up mirror and monitoring ports on the core switch to analyze mirrored traffic for access control. This method does not affect the existing network architecture and requires the core switch to support port mirroring.
